Targeted Muscle Reinnervation of the Foot for Morton's Neuroma—An Anatomic Study
Jessica Luo, BS1, Robert Kim, MD1, Chad Taylor, BS1, Mark A. Mahan, MD2 and Shaun D. Mendenhall, MD1, (1)University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, (2)Department of Neurosurgery, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT
Introduction:
Morton's neuroma is a common metatarsalgia that has high recurrence rates after neurectomy. Targeted muscle reinnervation (TMR) has recently emerged as a promising alternative surgical technique for treating symptomatic neuromas. The technique involves transfer of a problematic mixed or sensory nerve to a nearby redundant motor nerve branch. The purpose of this anatomic study was to identify potential motor nerve targets close to the location of Morton's neuromas for targeted muscle reinnervation.
Materials & Methods:
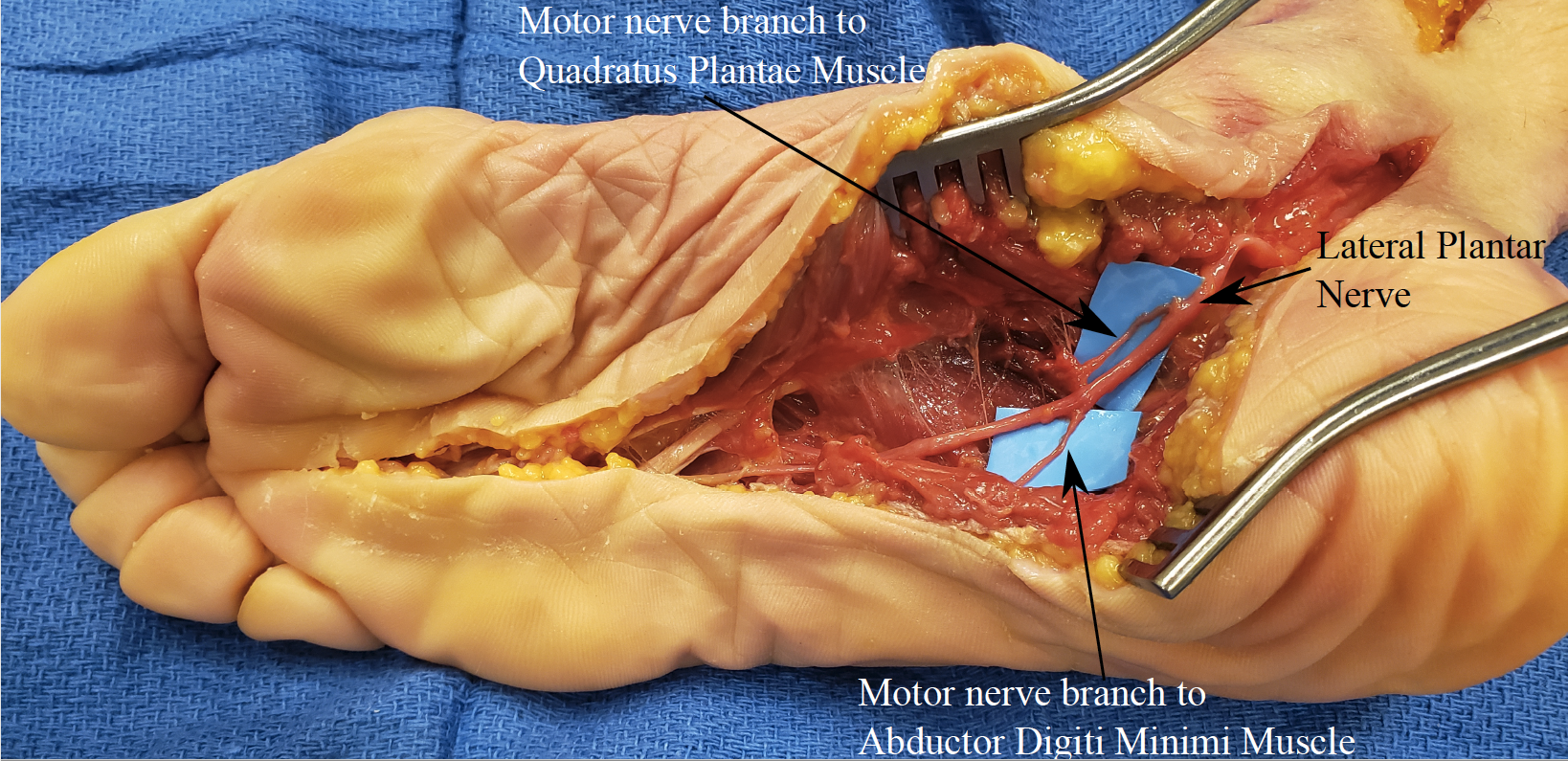
A plantar incision on the lateral part of the non-weight bearing instep of the foot was made to identify motor entry points (MEP) to intrinsic foot muscles in six fresh-frozen cadavers. Identification of the muscle, surface of the muscle belly that the MEP enters, diameter of the MEP, and ratio of the distance from the posterior aspect of the calcaneus to the fourth metatarsophalangeal joint was recorded for each MEP. The diameter of the common digital nerve to the third web space (most common site of Morton's neuroma) was measured before the bifurcation into proper plantar digital nerves.
Results:
The MEPs for the flexor digitorum brevis and abductor digiti minimi muscles were most consistently identified via the lateral instep incision. The abductor digiti minimi MEP was found in three cadavers entering the medial surface of the muscle belly. The diameters of the MEPs were <1mm. To provide location independent of foot length, the MEPs were found 57.9% (range: 48.0% - 64.4%) along a line from the posterior aspect of the calcaneus to the metatarsophalangeal joint (PC-MTPjt). The MEP for the flexor digitorum brevis was found in three cadavers entering the dorsolateral aspect of the muscle belly. Diameters of the MEPs ranged from >1mm to 2mm. The MEPs were found 45.2% (range: 43.9% - 47.6%) along the PC-MTPjt line. The diameter of the common plantar digital nerve ranged from 2-5mm and had evidence of entrapment/swelling in 2/6 cadavers. Coaptation between the common digital nerve and MEPs of both muscle was performed without tension.
Conclusion:
TMR for Morton's neuroma is feasible with consistent motor branches to the flexor digitorum brevis or abductor digiti minimi muscles. The flexor digitorum brevis MEP was more consistent in location and had a larger cross-sectional area, which makes this motor branch a reasonable target for TMR.
Back to 2021 ePosters
