Combined Local Delivery of Tacrolimus and Stem Cells in Fibrin Gel Is a Viable Potential Treatment for Enhancing Peripheral Nerve Regeneration
Mana Saffari, MD1,2, Katelyn Chan, MASc BioSci3, Sara Saffari, MD1,2, Kevin J. Zuo, MD, MASc4, Gregory H Borschel, MD5 and Alexander Y Shin, MD6, (1)Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, (2)Radboudumc, Nijmegen, Netherlands, (3)Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON, Canada, (4)University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, (5)Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, (6)Orthopaedic Surgery, Div Hand Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: The immunosuppressive and neuroregenerative potential of tacrolimus (FK506) may overcome the rejection of stem cells to enhance nerve regeneration. The aim of this study was to determine the feasibility and effectiveness of combining local, sustained delivery of tacrolimus (FK506) with stem cells.
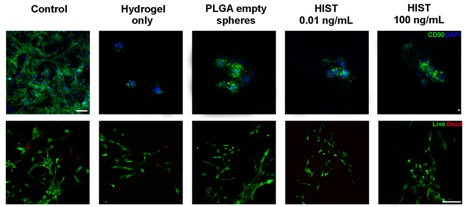
Materials & Methods: The drug release profile of local FK506 over the course of 35 days was evaluated. FK506 was incorporated into fibrin gel in poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) microspheres in concentrations of 0.01 ng/mL and 100 ng/mL and incubated in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at physiological temperature. Microspheres were prepared and characterized according to validated protocols by Tajdaran et al. (2015). PBS was replenished and collected every three days and analyzed on FK506 content using mass spectrometry. Adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) were cultured in collected PBS to mimic systemic exposure representing released concentrations at day 7, 15 and 28 from 0.01 ng/mL and 100 ng/mL microspheres. MSCs were cultured in the following groups: (i) hydrogel only, (ii) PLGA empty microspheres in hydrogel, (iii) Hydrogel Infused with Stem cells and Tacrolimus (HIST) 0.01 ng/mL, and (iv) HIST 100 ng/mL. Staining against CD90 was conducted to confirm stem cell characterization. MSC viability was evaluated at 24h, 48h, 72h, and seven days using Live/dead staining and MTS assays, and expressed as a ratio of the activity of MSCs cultured in media without FK506 (control).
Results: Microspheres containing 0.01 ng/mL showed depletion of FK506 by 13 days. FK506 microspheres containing 100 ng/mL revealed a sustained release up to 35 days, with a cumulative mass of 200 mg for the duration of the study. An inflation point was observed at day 15 due to erosion of gel, resulting in an increase of FK506 release. The release profile was consistent and comparable with previous studies. CD90 staining confirmed stem cell characterization. The MSC viability ratio confirmed viability up to seven days and was found to be approximately 80% and 100% when MSCs were cultured in collected PBS and were seeded in hydrogel groups, respectively. No significant differences in viability were found between groups.
Conclusions: Encapsulation of 100 ng/mL FK506 microspheres and MSCs in hydrogel is feasible and has strong potential to enhance survival of transplanted cells, which may ultimately lead to improved nerve regeneration.
Back to 2021 Abstracts
