Sutureless Approach Using Vein Grafts In Peripheral Nerve Repair: Functional and Immunohistological Results
Ali Eren, MD1; Sacit Turanli, MD1; Cemile Merve Seymen, PhD1; Ferda Alpaslan Pinarli, MD, PhD2; Gülnur Take Kaplanoglu, PhD1
1Gazi University, Ankara, Turkey, 2Diskapi Yildirim Beyazit Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
Purpose: The aim of this study was to define a sutureless peripheral nerve repair technique using a vein graft and compare it to epineural repair. The vein grafts were also used as a reservoir for bone marrow-derived stem cells (BMSC) and stem cell effects on primary nerve repair were investigated.
Methods: Thirty Wistar Albino rats were randomly divided into five groups. The sciatic nerve was transected. In the first group (K), epineural repair was performed. In the second group (SV), epineural repair was wrapped with a vein graft. In the third group (MSV), epineural repair was wrapped with a vein graft and BMSCs were injected into the vein. In the fourth group (V), sutureless repair using vein graft was performed. (Fig 1) In the fifth group (MV), sutureless repair using vein graft was performed and BMSCs were injected. Functional recovery was evaluated with pinprick, toe spread tests and sciatic nerve index (SFI). Nerve regeneration was also assessed by gastrocnemius index and immunohistochemical analysis.
Results: There was no difference in pinprick and toe spread tests between the groups. SFI revealed no difference at 4th and 8th weeks, however, at the 12th week, all other groups showed better improvement compared to epineural repair where the MSV revealed the best (p<0.05). (K: -76.5±3.7, SV: -65.2±11.7, MSV: -46.2±19.4, V: -68.8±9.8, MV: -56±8.8) (Fig 2) There was no difference in gastrocnemius index between the groups. Better immunoreaction in GAP-43 and NF-H staining, which were the indicators of nerve regeneration, was observed in MSV, MV, SV, V groups respectively, that MSV showed the best (p<0.05). (Fig 3) SV and MSV groups showed less fibrosis area (K: 221.5 ± 25.9, SV: 101.6 ± 7.1, MSV: 121.3±18.8, V: 150.3 ± 12.1, MV: 152.4 ± 11.8 µm2, p<0.05) and MSV group had better alignment compared to other groups.
Conclusions: Although sutureless repair with a vein graft reveals better functional results compared to epineural repair, epineural suture repair before vein wrapping improves the functional and immunohistochemical results and decreases fibrosis. BMSCs also improves regeneration in primary peripheral nerve repair.
Key words: Sutureless nerve repair, peripheral nerve injury, vein graft, mesenchymal stem cell
Figure 1: Sutureless repair technique with vein graft. Sutures (Black arrows) have been taken away from the regeneration site.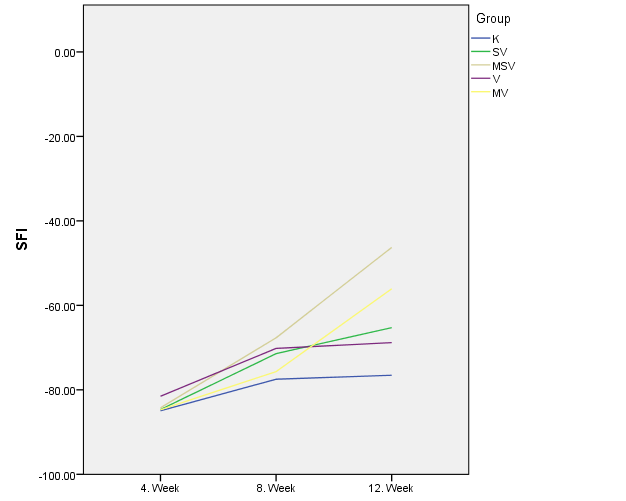
Figure 2: Sciatic functional index (SFI) results of the groups
Figure 3: Hematoxylin&eosin (H&E), GAP-43, NF-H staining results of the groups.
Back to 2018 ePosters
